In the wave of global energy transformation, photovoltaic (PV) technology has emerged as a core force driving green development. As a foreign trade enterprise deeply rooted in the new energy sector, Solarway New Energy closely follows industry trends and is committed to providing global customers with efficient, reliable off-grid photovoltaic power solutions. Today, we will walk you through the principles, application scenarios, and future trends of photovoltaic power generation in a simple, easy-to-understand way.
I. Photovoltaic Power Generation: How Is Sunlight Converted into Electricity?
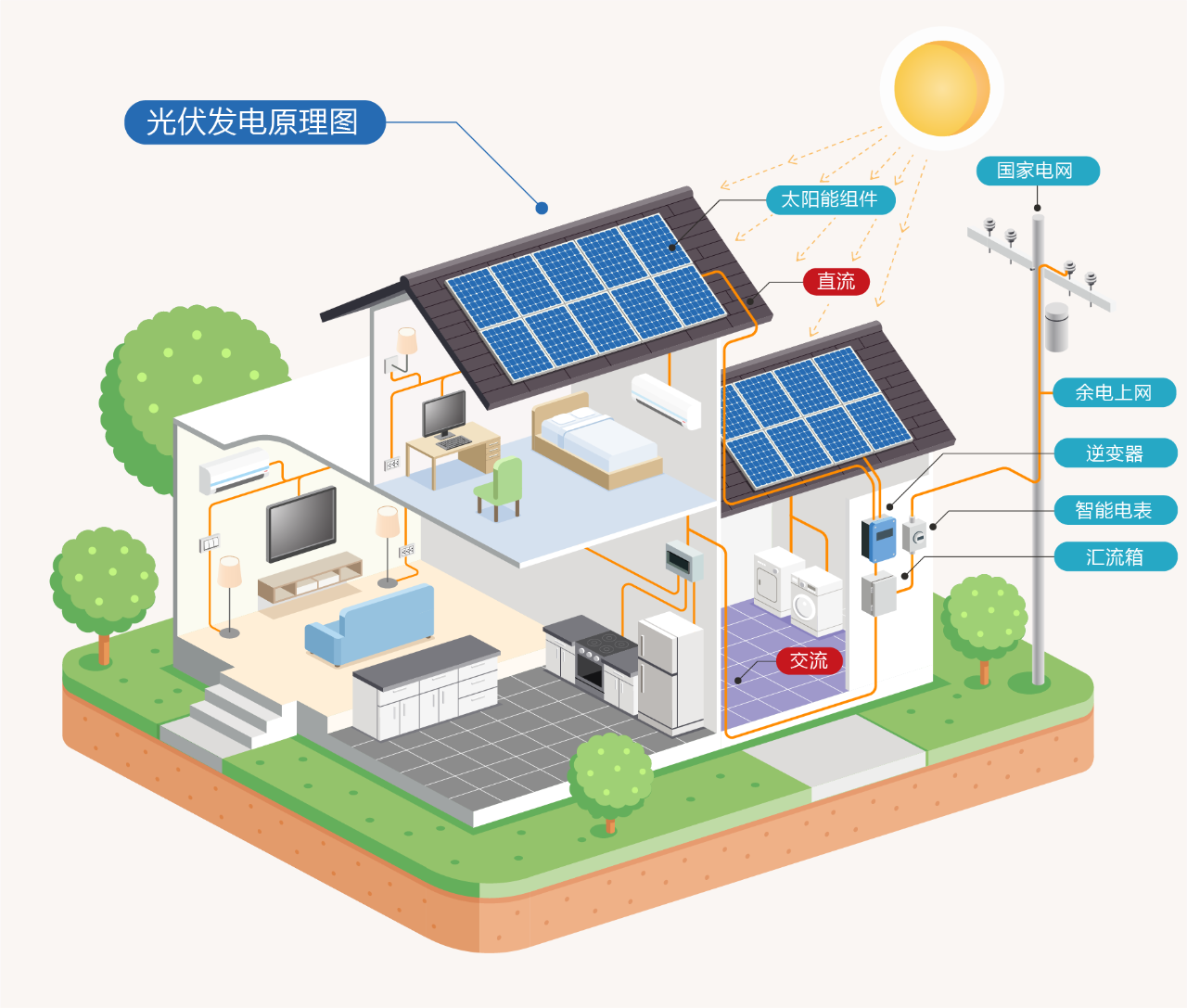
The core principle of photovoltaic power generation is the photovoltaic effect—when sunlight strikes semiconductor materials (such as silicon), photons excite electrons within the material, generating an electric current. This process requires no mechanical movement or chemical fuel, enabling truly zero-emission clean energy production.
Key Component Overview:
Photovoltaic Modules (Solar Panels): Comprising multiple solar cells connected in series or parallel, these modules convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter: Converts DC into alternating current (AC), ensuring the electricity is compatible with grid systems or household appliances.
Mounting System: Secures the modules and optimizes their angle for maximum sunlight exposure, improving overall efficiency.
Energy Storage Equipment (Optional): Stores excess electricity to mitigate the intermittent nature of solar power generation.
Power Generation Flow:
Photovoltaic modules absorb sunlight → Generate DC → Inverter converts to AC → Electricity is either fed into the grid or used directly.
-
II. Photovoltaic Applications: From Homes to Heavy Industry
Photovoltaic technology is now integrated into many areas of daily life, serving as a key pillar in the global energy transition.
1. Residential Photovoltaics: The “Money-Making Machine” on Your Roof
Model: Self-consumption with surplus power fed into the grid, or full-grid connection.
Benefits: A 10kW residential PV system typically generates around 40 kWh per day. Annual revenue can reach up to 12,000 yuan, with a payback period of 6–8 years and a system lifespan exceeding 25 years.
Case Study: In European countries like Germany and the Netherlands, residential PV penetration exceeds 30%, making it a preferred choice for reducing energy costs and carbon emissions.
2. Commercial and Industrial Photovoltaics: A Powerful Tool for Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Challenges: In energy-intensive industries, electricity can account for over 30% of total costs. PV systems can reduce these costs by 20%–40%.
Innovative Models:
“Photovoltaic + Steam”: Aluminum plants use solar power to generate steam, cutting production costs by 200 yuan per ton.
“Photovoltaic + Charging Stations”: Logistics parks utilize solar-generated electricity to power EV charging stations, generating revenue through price differentials and service fees.
3. Centralized Photovoltaic Power Plants: The Backbone of Large-Scale Clean Energy
Site Selection: Optimal in regions with abundant sunlight, such as deserts and Gobi areas.
Scale: Systems often range from megawatts to hundreds of megawatts.
Case Study: The Taratang PV power plant in Qinghai, China, has an installed capacity of over 10 GW and generates more than 15 billion kWh annually—reducing carbon emissions by 1.2 million tonnes per year.
III. Photovoltaic Technology Trends: Innovation Leading the Way
1. High-Efficiency PV Cell Technologies
PERC Cells: The current mainstream, with 22%–24% efficiency, widely used in large-scale installations.
N-Type Cells (TOPCon/HJT): Higher efficiency (26%–28%) with better high-temperature performance, ideal for C&I rooftops.
Perovskite Tandem Cells: Lab-tested efficiencies exceed 33%; lightweight and flexible but with limited durability (5–10 years). Not yet mass-produced as of 2025.
2. Integration with Energy Storage
PV + storage is increasingly standard, with policies mandating 15%–25% storage integration. In the C&I segment, energy storage solutions have internal rates of return (IRR) above 12%.
3. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Combines PV modules with building materials—such as rooftops and curtain walls—providing both functionality and aesthetic value.
IV. Solarway New Energy: A Global Contributor in Photovoltaic Development
As a foreign trade enterprise specializing in off-grid photovoltaic conversion equipment, Solarway New Energy offers a product line that includes inverters, solar controllers, and portable power stations. Our products are exported to countries including Germany, France, the Netherlands, and the United States.
We uphold a vision of “providing high-quality products to meet power needs in mobile living,” offering customers dependable and efficient solutions.
Our Advantages:
Technical Capabilities: Home to a dedicated technology center, the company has secured 51 patents and 6 software copyrights.
Quality Assurance: Certified under ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 systems, with international product certifications including CE, ROHS, and ETL.
Global Reach: After-sales service centers have been established in Leipzig, Germany, and Malta to ensure localized customer support.
Photovoltaic technology is not only at the heart of the global energy transition but also a driving force in the fight against climate change and the pursuit of sustainable development. From residential rooftops to industrial parks, from vast desert plants to city buildings, solar power is reshaping the energy landscape and illuminating a cleaner, brighter future.
Post time: Jun-23-2025